Wifi vs Mobile Data
The debate between Wifi and mobile data has been ongoing for years, with each having its own set of advantages and disadvantages. As the world becomes increasingly dependent on internet connectivity, understanding the differences between these two technologies is crucial for making informed decisions about how to stay connected. In this article, we will delve into the world of Wifi and mobile data, exploring their strengths, weaknesses, and the scenarios in which one is preferable to the other.
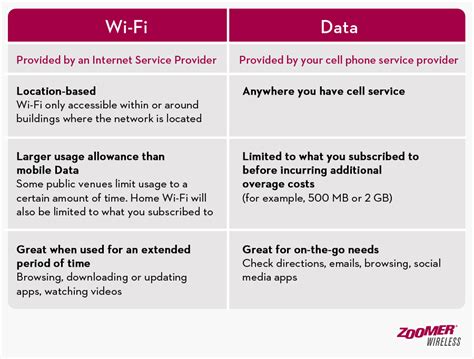
Wifi, short for Wireless Fidelity, is a type of wireless networking technology that allows devices to connect to the internet or communicate with each other without the use of cables or wires. Wifi networks operate on a specific frequency band, typically 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz, and use radio waves to transmit data between devices. On the other hand, mobile data, also known as cellular data, refers to the ability to access the internet through a cellular network, such as 3G, 4G, or 5G. Mobile data uses cell towers to provide coverage, allowing users to access the internet from anywhere within the network's range.
Key Points
- Wifi is generally faster and more reliable than mobile data, but its range is limited to the network's coverage area.
- Mobile data provides greater mobility and flexibility, but its speed and reliability can be affected by network congestion and signal strength.
- The cost of Wifi and mobile data can vary depending on the provider, plan, and usage, with Wifi often being more cost-effective for heavy users.
- Security is a major concern for both Wifi and mobile data, with public Wifi networks being more vulnerable to hacking and mobile data being susceptible to interception.
- The choice between Wifi and mobile data ultimately depends on the user's specific needs and circumstances, with a combination of both often being the most effective solution.
Speed and Reliability

One of the primary advantages of Wifi is its speed and reliability. Wifi networks can offer speeds of up to 1 Gbps (gigabit per second), making them ideal for heavy internet users who need to stream videos, play online games, or transfer large files. In contrast, mobile data speeds can vary greatly depending on the network and location, with average speeds ranging from 10-100 Mbps (megabits per second). However, with the advent of 5G technology, mobile data speeds are expected to increase significantly, potentially rivaling those of Wifi.
In terms of reliability, Wifi networks are generally more stable and less prone to outages than mobile data. This is because Wifi networks are typically connected to a physical infrastructure, such as a router or modem, which provides a more stable connection. Mobile data, on the other hand, relies on cell towers and can be affected by factors such as network congestion, signal strength, and physical obstacles.
Cost and Coverage
The cost of Wifi and mobile data can vary greatly depending on the provider, plan, and usage. Wifi is often more cost-effective for heavy users, as it typically offers unlimited data plans and faster speeds. Mobile data, on the other hand, can be more expensive, especially for heavy users, as it often comes with data caps and slower speeds. However, mobile data provides greater mobility and flexibility, allowing users to access the internet from anywhere within the network’s range.
In terms of coverage, mobile data has a clear advantage over Wifi. Mobile data networks cover a much wider area, including rural and remote regions, making it possible to access the internet from almost anywhere. Wifi networks, on the other hand, are typically limited to a specific coverage area, such as a home or office building.
| Technology | Speed | Reliability | Cost | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wifi | Up to 1 Gbps | High | Low | Limited |
| Mobile Data | Up to 100 Mbps | Medium | High | Wide |

Security and Privacy

Security and privacy are major concerns for both Wifi and mobile data. Public Wifi networks, in particular, are vulnerable to hacking and eavesdropping, as they often lack the security measures of private networks. Mobile data, on the other hand, is susceptible to interception and surveillance, especially in areas with weak network security.
To mitigate these risks, users can take several precautions, such as using virtual private networks (VPNs), encrypting data, and avoiding public Wifi networks. Additionally, mobile data users can use secure protocols, such as HTTPS, to protect their data from interception.
Future Developments
The future of Wifi and mobile data is exciting and rapidly evolving. With the advent of 5G technology, mobile data speeds are expected to increase significantly, potentially rivaling those of Wifi. Additionally, the development of new Wifi standards, such as Wifi 6, promises to improve the speed and reliability of Wifi networks.
Furthermore, the increasing use of internet of things (IoT) devices and the growth of smart cities are expected to drive the demand for faster and more reliable internet connectivity. As a result, both Wifi and mobile data are likely to play a critical role in meeting this demand and enabling the widespread adoption of IoT devices and smart city technologies.
What is the main difference between Wifi and mobile data?
+The main difference between Wifi and mobile data is the way they provide internet connectivity. Wifi uses radio waves to connect devices to a network, while mobile data uses cell towers to provide coverage.
Which is faster, Wifi or mobile data?
+Wifi is generally faster than mobile data, with speeds of up to 1 Gbps. However, mobile data speeds are improving with the advent of 5G technology.
Is Wifi more secure than mobile data?
+Wifi can be more secure than mobile data if it is properly configured and secured. However, public Wifi networks are vulnerable to hacking and eavesdropping, while mobile data is susceptible to interception and surveillance.
In conclusion, the choice between Wifi and mobile data depends on the user’s specific needs and circumstances. While Wifi offers faster speeds and greater reliability, mobile data provides greater mobility and flexibility. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each technology, users can make informed decisions about how to stay connected and access the internet. As the world becomes increasingly dependent on internet connectivity, the importance of Wifi and mobile data will only continue to grow, driving innovation and advancements in the field of networking and telecommunications.



