Mobile App vs Web App
The debate between mobile apps and web apps has been ongoing for several years, with each side having its own set of advantages and disadvantages. As technology continues to evolve, it's essential to understand the differences between these two types of applications and determine which one is best suited for your specific needs. In this article, we'll delve into the world of mobile and web apps, exploring their characteristics, benefits, and drawbacks, as well as the current trends and future prospects.
Key Points
- Mobile apps offer native performance, personalized experience, and offline capabilities
- Web apps provide cross-platform compatibility, ease of maintenance, and cost-effectiveness
- Hybrid apps combine the benefits of mobile and web apps, offering a compromise between the two
- Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) are emerging as a popular choice, offering a seamless user experience
- The choice between mobile and web apps depends on factors such as target audience, functionality, and development resources
Mobile Apps

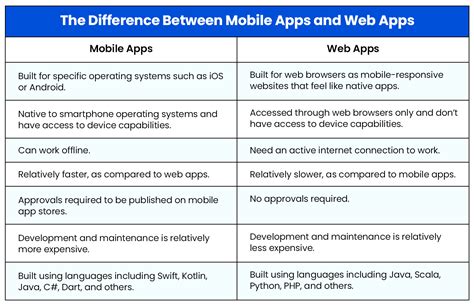
Mobile apps are software applications designed to run on mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. They are typically developed using native programming languages, such as Java or Swift, and are distributed through app stores like Apple App Store or Google Play. Mobile apps are optimized for mobile devices, offering a personalized and immersive user experience. They can access device hardware, such as cameras and GPS, and provide offline capabilities, making them ideal for applications that require frequent use or have specific hardware requirements.
Advantages of Mobile Apps
Mobile apps have several advantages, including:
- Native Performance: Mobile apps are optimized for mobile devices, providing fast and seamless performance
- Personalized Experience: Mobile apps can access device hardware and provide a tailored experience based on user preferences and behavior
- Offline Capabilities: Mobile apps can function offline, making them ideal for applications that require frequent use or have limited internet connectivity
Disadvantages of Mobile Apps
However, mobile apps also have some disadvantages, including:
- Development Complexity: Developing mobile apps can be time-consuming and require significant resources, especially when developing for multiple platforms
- App Store Approval: Mobile apps must be approved by app stores, which can be a lengthy and uncertain process
- Maintenance and Updates: Mobile apps require regular maintenance and updates, which can be costly and time-consuming
Web Apps

Web apps, on the other hand, are software applications that run on web browsers, such as Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox. They are typically developed using web technologies, such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, and are accessed through a URL. Web apps are cross-platform compatible, meaning they can run on multiple devices and operating systems, making them ideal for applications that require broad accessibility.
Advantages of Web Apps
Web apps have several advantages, including:
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Web apps can run on multiple devices and operating systems, making them ideal for applications that require broad accessibility
- Ease of Maintenance: Web apps are easier to maintain and update, as changes can be made on the server-side without requiring user intervention
- Cost-Effectiveness: Web apps are generally less expensive to develop and maintain than mobile apps, as they don’t require native programming languages or app store approval
Disadvantages of Web Apps
However, web apps also have some disadvantages, including:
- Performance Limitations: Web apps can be slower and less responsive than mobile apps, due to the limitations of web technologies and internet connectivity
- Limited Hardware Access: Web apps have limited access to device hardware, making them less suitable for applications that require specific hardware features
- Security Concerns: Web apps can be more vulnerable to security threats, such as hacking and data breaches, due to the open nature of the web
Hybrid Apps
Hybrid apps are a compromise between mobile and web apps, offering a combination of the benefits of both. They are developed using web technologies, such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, but are wrapped in a native shell, allowing them to access device hardware and provide a more personalized experience. Hybrid apps are ideal for applications that require the benefits of both mobile and web apps, such as cross-platform compatibility and native performance.
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) are a type of web app that provides a seamless user experience, similar to mobile apps. They are developed using web technologies, such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, but are optimized for mobile devices, offering features such as offline capabilities, push notifications, and home screen installation. PWAs are emerging as a popular choice for applications that require a mobile-like experience, without the need for native programming languages or app store approval.
| App Type | Characteristics | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mobile Apps | Native programming languages, device-specific | Native performance, personalized experience, offline capabilities | Development complexity, app store approval, maintenance and updates |
| Web Apps | Web technologies, cross-platform compatible | Cross-platform compatibility, ease of maintenance, cost-effectiveness | Performance limitations, limited hardware access, security concerns |
| Hybrid Apps | Web technologies, native shell | Cross-platform compatibility, native performance, personalized experience | Development complexity, limited hardware access, security concerns |
| Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) | Web technologies, optimized for mobile devices | Seamless user experience, offline capabilities, push notifications | Performance limitations, limited hardware access, security concerns |

What is the main difference between mobile and web apps?
+The main difference between mobile and web apps is that mobile apps are designed to run on mobile devices, while web apps are designed to run on web browsers. Mobile apps are typically developed using native programming languages, while web apps are developed using web technologies.
What are the advantages of hybrid apps?
+Hybrid apps offer a combination of the benefits of mobile and web apps, including cross-platform compatibility, native performance, and personalized experience. They are ideal for applications that require the benefits of both mobile and web apps.
What is the future of mobile and web apps?
+The future of mobile and web apps is likely to be shaped by emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and the Internet of Things (IoT). As these technologies continue to evolve, we can expect to see new and innovative applications that blur the lines between mobile and web apps.



