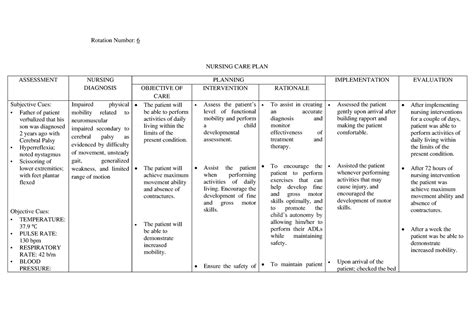
Impaired Bed Mobility Nursing Diagnosis

Impaired bed mobility is a common issue faced by patients who are hospitalized or residing in long-term care facilities. This condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including but not limited to, musculoskeletal disorders, neurological conditions, cardiovascular diseases, and surgical procedures. As a result, patients may experience difficulty moving in bed, transferring, or performing daily activities, which can lead to a range of complications, including pressure ulcers, pneumonia, and decreased functional ability. In this article, we will explore the concept of impaired bed mobility, its causes, and the nursing diagnosis and interventions that can be used to address this issue.
Key Points
- Impaired bed mobility is a common issue that can lead to a range of complications, including pressure ulcers and pneumonia.
- The causes of impaired bed mobility include musculoskeletal disorders, neurological conditions, cardiovascular diseases, and surgical procedures.
- Nursing diagnosis for impaired bed mobility involves assessing the patient's ability to move in bed, transfer, and perform daily activities.
- Interventions for impaired bed mobility include positioning, transferring, and mobility aids, as well as education and support for patients and their families.
- Early identification and intervention are critical to preventing complications and promoting optimal outcomes for patients with impaired bed mobility.
Causes of Impaired Bed Mobility

Impaired bed mobility can be caused by a variety of factors, including musculoskeletal disorders, such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and osteoporosis. Neurological conditions, such as stroke, spinal cord injury, and Parkinson’s disease, can also impair bed mobility. Additionally, cardiovascular diseases, such as heart failure and peripheral artery disease, can cause impaired bed mobility due to decreased mobility and endurance. Surgical procedures, such as hip replacement and spinal surgery, can also cause impaired bed mobility due to post-operative pain and discomfort.
Nursing Diagnosis for Impaired Bed Mobility
The nursing diagnosis for impaired bed mobility involves assessing the patient’s ability to move in bed, transfer, and perform daily activities. This assessment should include an evaluation of the patient’s strength, range of motion, balance, and coordination, as well as their ability to perform activities of daily living (ADLs), such as bathing, dressing, and toileting. The nurse should also assess the patient’s pain level, comfort, and overall well-being, as these factors can impact their ability to move and perform daily activities.
| Assessment Criteria | Evaluation Method |
|---|---|
| Strength | Manual muscle testing, observation of movement |
| Range of motion | Passive and active range of motion exercises |
| Balance and coordination | Observation of movement, balance tests |
| ADLs | Observation of patient performing ADLs, patient self-report |
| Pain level | Pain assessment tools, patient self-report |
Interventions for Impaired Bed Mobility
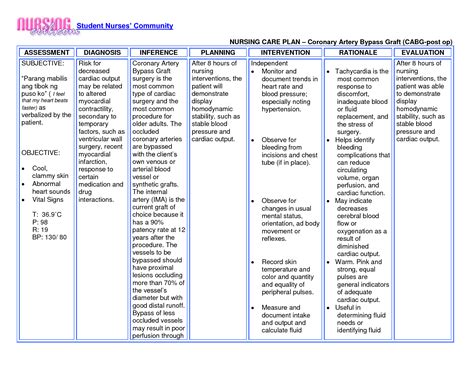
Interventions for impaired bed mobility should be individualized to meet the patient’s specific needs and goals. Positioning, transferring, and mobility aids, such as bed rails, transfer belts, and walkers, can be used to support the patient’s movement and prevent complications. Education and support for patients and their families are also essential to promote optimal outcomes and prevent complications. This can include teaching the patient and their family how to move safely, use mobility aids, and perform daily activities.
Positioning and Transferring
Positioning and transferring are critical interventions for impaired bed mobility. The nurse should use proper technique when positioning and transferring the patient to prevent injury and promote comfort. This can include using a transfer belt, lifting the patient’s legs when transferring, and using a slide board or transfer mat to reduce friction and prevent skin shear.
Mobility Aids
Mobility aids, such as bed rails, transfer belts, and walkers, can be used to support the patient’s movement and prevent complications. The nurse should assess the patient’s need for mobility aids and provide education on their proper use. This can include demonstrating how to use the mobility aid, providing written instructions, and monitoring the patient’s use of the mobility aid.
What are the most common causes of impaired bed mobility?
+The most common causes of impaired bed mobility include musculoskeletal disorders, neurological conditions, cardiovascular diseases, and surgical procedures.
How can nurses assess impaired bed mobility?
+Nurses can assess impaired bed mobility by evaluating the patient's strength, range of motion, balance, and coordination, as well as their ability to perform ADLs and their pain level.
What interventions can be used to address impaired bed mobility?
+Interventions for impaired bed mobility include positioning, transferring, and mobility aids, as well as education and support for patients and their families.
In conclusion, impaired bed mobility is a common issue that can lead to a range of complications, including pressure ulcers and pneumonia. The causes of impaired bed mobility include musculoskeletal disorders, neurological conditions, cardiovascular diseases, and surgical procedures. Nursing diagnosis for impaired bed mobility involves assessing the patient’s ability to move in bed, transfer, and perform daily activities. Interventions for impaired bed mobility should be individualized to meet the patient’s specific needs and goals, and may include positioning, transferring, and mobility aids, as well as education and support for patients and their families. Early identification and intervention are critical to preventing complications and promoting optimal outcomes for patients with impaired bed mobility.