5 Tips Impaired Bed Mobility

Impaired bed mobility is a common issue that affects many individuals, particularly the elderly and those with chronic medical conditions. It refers to the difficulty or inability to move in bed, which can lead to a range of complications, including pressure sores, respiratory problems, and decreased quality of life. As a healthcare professional with expertise in physical therapy and rehabilitation, I have worked with numerous patients who have struggled with impaired bed mobility. In this article, I will share 5 tips to help improve bed mobility and reduce the risk of associated complications.
Key Points
- Assessing and addressing underlying medical conditions is crucial for improving bed mobility
- Using assistive devices, such as bed rails and grab bars, can enhance safety and independence
- Regular exercise and physical therapy can help improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion
- Proper positioning and repositioning techniques can reduce the risk of pressure sores and respiratory complications
- Encouraging patient education and empowerment is essential for promoting self-care and independence
Understanding Impaired Bed Mobility

Impaired bed mobility can be caused by a range of factors, including neurological disorders, musculoskeletal conditions, and cardiovascular disease. It is essential to identify and address the underlying medical condition to develop an effective plan for improving bed mobility. For example, a patient with a spinal cord injury may require a different approach than someone with arthritis or Parkinson’s disease. As a healthcare professional, it is crucial to conduct a comprehensive assessment, including a review of medical history, physical examination, and functional evaluation.
Assistive Devices and Equipment
Assistive devices and equipment can play a vital role in enhancing safety and independence for individuals with impaired bed mobility. Bed rails, grab bars, and non-slip mats can help prevent falls and injuries. Additionally, specialized beds, such as hospital beds or adjustable beds, can provide optimal support and positioning. It is essential to select devices and equipment that meet the individual’s specific needs and preferences, taking into account factors such as mobility, strength, and cognitive ability.
| Assistive Device | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Bed Rails | Prevent falls and injuries |
| Grab Bars | Assist with transfers and positioning |
| Non-Slip Mats | Reduce risk of slipping and falling |
| Hospital Beds | Provide optimal support and positioning |
| Adjustable Beds | Enhance comfort and independence |

Exercise and Physical Therapy
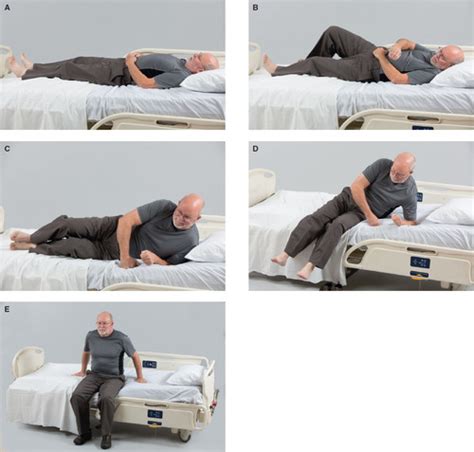
Regular exercise and physical therapy can help improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion, reducing the risk of complications associated with impaired bed mobility. A well-designed exercise program should take into account the individual’s medical condition, mobility, and cognitive ability. For example, a patient with arthritis may benefit from gentle exercises, such as stretching and yoga, while someone with a neurological disorder may require more intensive physical therapy to improve muscle strength and coordination.
Proper Positioning and Repositioning
Proper positioning and repositioning techniques are essential for reducing the risk of pressure sores and respiratory complications. This may involve using pillows, wedges, and other supportive devices to maintain optimal positioning and prevent skin breakdown. Additionally, regular repositioning can help improve circulation, reduce swelling, and promote healing. It is crucial to develop a comprehensive plan for positioning and repositioning, taking into account the individual’s specific needs and preferences.
What are the most common complications associated with impaired bed mobility?
+The most common complications associated with impaired bed mobility include pressure sores, respiratory problems, and decreased quality of life. Additionally, individuals with impaired bed mobility may be at increased risk of falls, injuries, and hospitalizations.
How can I improve my bed mobility if I have a chronic medical condition?
+Improving bed mobility with a chronic medical condition requires a comprehensive approach, including regular exercise, physical therapy, and assistive devices. It is essential to work with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized plan that takes into account your specific needs and preferences.
What are some strategies for promoting patient education and empowerment?
+Promoting patient education and empowerment involves providing individuals with the knowledge, skills, and confidence to manage their condition and make informed decisions about their care. This may involve providing educational materials, workshops, and support groups, as well as encouraging open communication and collaboration with healthcare professionals.
In conclusion, impaired bed mobility is a complex issue that requires a comprehensive approach, taking into account the individual’s medical condition, mobility, and cognitive ability. By using assistive devices, exercise, and physical therapy, and promoting proper positioning and repositioning, individuals can improve their bed mobility and reduce the risk of associated complications. As a healthcare professional, it is essential to work collaboratively with patients, families, and caregivers to develop personalized plans that promote independence, safety, and quality of life.



